
 back to all news
back to all news
A Circular Economy Framework for Automobiles
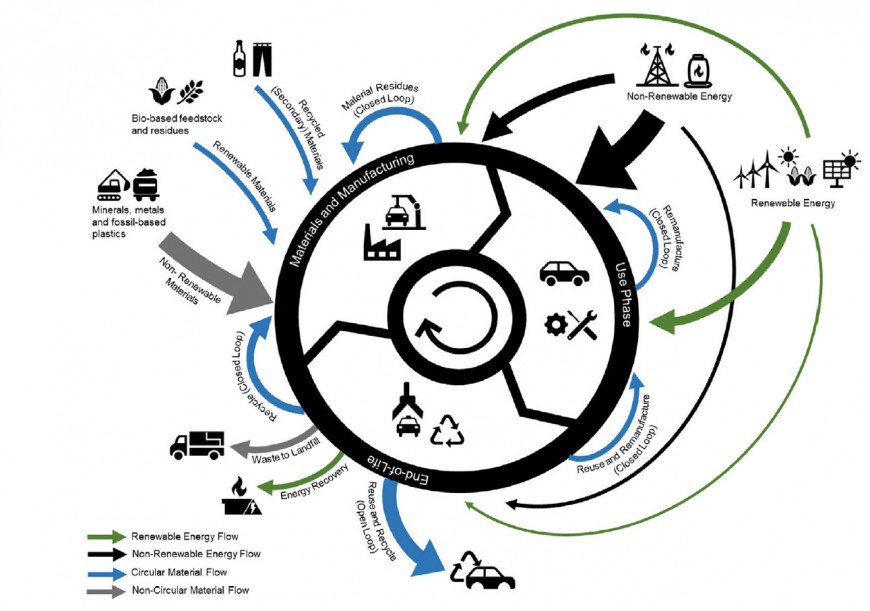
Today’s automobiles rely heavily on the extraction of virgin raw materials for manufacturing and fossil fuels for vehicle operation. However, industry investment in vehicle electrification will lead to greater renewable energy use, and manufacturers are reducing reliance on virgin raw materials by increasing recycled content.
This increased emphasis on renewables and recycling—two key strategies of what is known as the automotive circular economy—provides a path toward greater product sustainability across the industry, according to Greg Keoleian of the University of Michigan School for Environment and Sustainability.
In a paper published online Nov. 20 in the Journal of Industrial Ecology, Keoleian, University of Michigan researchers, and colleagues at Ford Motor Company present the first circular economy framework for automobiles.
“Corporations, including automotive manufacturers, are increasingly exploring circular economy strategies as a means to enhance the sustainability of their products,” said Keoleian, the study’s senior author. “The circular economy paradigm focuses on reducing non-renewable materials and energy, promoting renewable feedstocks and energy, and keeping products/materials in use across the life cycle of a system. As such, life cycle environmental burdens associated with vehicle manufacturing, use, and disposal could potentially be reduced through circular economy strategies.
“Circular economy of autos today is mixed but future circularity is promising,” added Keoleian.
The study evaluated key circular economy metrics and found that:
- About 6% of the energy currently used to make, operate, and dispose of U.S. internal combustion engine sedans comes from renewable sources. E10 gasoline, which contains 10% ethanol by volume, is the main renewable energy source.
- About 8% of the energy currently used to make, operate, and dispose of U.S. battery electric vehicles comes from renewable sources. Most of that renewable energy comes from wind, hydropower, and solar on the electrical grid used to charge the vehicles. As utilities install more solar and wind, that percentage will rise.
- U.S. internal combustion engine sedans use about 27% recycled materials, while battery electric vehicles use about 21% recycled materials.
- Due to their high metal content, automobiles are among the most-recycled products, with about 95% of automobiles recycled to some degree. However, plastics, rubber, foam, residual metal pieces, paper, fabric, glass and other low-density materials are usually sent to landfills.
In addition, the researchers conducted a case study of Ford Motor Company and mapped their sustainability programs and initiatives using the circular economy schematic that they developed.
Aside from Keoleian, the other authors of the paper include Laura Cristina Aguilar Esteva, Akshat Kasliwal, Michael Kinzler (University of Michigan Center for Sustainable Systems), and Hyung Chul Kim (Ford Motor Company).
The Journal of Industrial Ecology paper is available here.

